Analog Inputs Low Signal
Description
This feature is present on all several modules:
OI-AnalogLS (x10)
The Analog Input Low Signal (AINLS) functionality provides high-precision signal acquisition for various sensor types including thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), and strain gauges. It delivers exceptional resolution for low-level signal detection and processing.
Key features:
16-bit resolution, corresponding to 76 μV (with gain = 1) or as low as 0.6 μV (with gain = 128)
10 analog inputs configurable as 5 differential analog input pairs
Integrated current generator for exciting passive sensors like 2-wire or 3-wire RTDs
Programmable Gain with settings from 1 to 128
For sensors like RTDs, a constant current source is necessary. To limit acquisition errors, the excitation current flows through a precision resistor, and the voltage across this resistor serves as the reference voltage for the digitization stage (ratiometric measurement).
When measuring differential pairs, the maximum voltage range is ±2.5V. Using the integrated programmable gain (with gains from 1 to 128), the maximum voltage range can be reduced to ±20mV. Using gain amplification for very low voltage signals increases precision while maintaining resolution.
Voltage Requirements:
When gain is disabled: Each analog input must be between -50mV and 5.05V relative to ground
When gain is 1 to 16: Input voltage range must be from (150mV + Vdiff,max * (Gain-1) / 2) to (4.85V – Vdiff,max * (Gain-1) / 2)
When gain is 32 to 128: Input voltage range must be from (150mV + 15.5 * Vdiff,max) to (4.85V – 15.5 * Vdiff,max)
The Analog Input Low Signal functionality integrates a matrix that establishes connections in the excitation multiplexers and sensor terminal block. These connections are physically implemented on the board and cannot be controlled through software.
The matrix is optimized to allow simultaneous reading of:
5 thermocouples, or
5 RTDs with 2 wires, or
3 RTDs with 3 wires, or
4 strain gauges excited by voltage, or
2 strain gauges excited by current
Reading different types of sensors simultaneously is possible if the sensor assignment on the terminal block is compatible with the existing matrix.
Connection example:
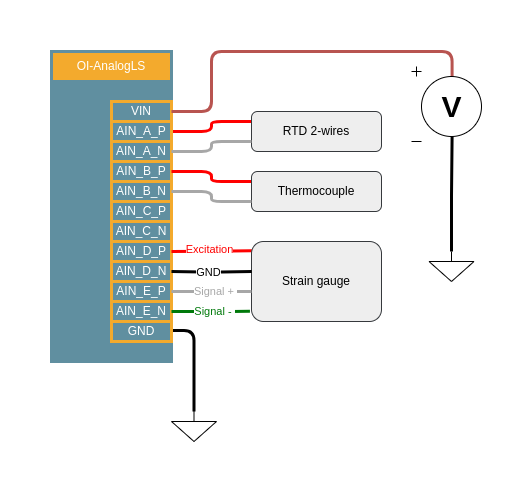
Characteristics
Characteristic |
Value |
Remark |
|---|---|---|
Resolution |
16-bit |
|
Input voltage range |
±2.5V (differential) |
|
Gain range |
1 to 128 |
|
Sampling rate |
Up to 4kSPS |
|
Supported sensors |
Thermocouples, RTDs (2-wire and 3-wire), Strain gauges |
|
Number of channels |
5 differential channels |
Code examples
Example: Reading RTD, Thermocouple and Strain Gauge Simultaneously
#include "OpenIndus.h"
#include "Arduino.h"
AnalogLS analogls;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello OpenIndus !\n");
delay(1000);
// Add a PT1000 RTD sensor (two wire)
analogls.addSensor(RTD_PT1000, {AIN_A_P, AIN_A_N});
analogls.sensors[0]->setAcquisitionTime(SAMPLE_50_MS);
analogls.sensors[0]->setStabilizationTime(50);
// Add a type K thermocouple
analogls.addSensor(THERMOCOUPLE_K, {AIN_B_P, AIN_B_N});
// Add a strain gauge: SIGNAL+, SIGNAL-, EXCIT+, EXCIT-
analogls.addSensor(STRAIN_GAUGE, {AIN_E_P, AIN_E_N, AIN_D_P, AIN_D_N});
}
void loop(void)
{
float data = 0.0;
// RTD sensor
data = analogls.sensors[0]->readTemperature();
Serial.printf(">RTD (CH0) - Temperature(°C): %.2f\n", data);
delay(200);
// Thermocouple
data = analogls.sensors[1]->readMillivolts();
Serial.printf(">TC (CH1) - Voltage (mV): %.2f\n", data);
data = analogls.sensors[1]->readTemperature();
Serial.printf(">TC (CH1) - Temperature (°C): %.2f\n", data);
// Strain gauge
data = analogls.sensors[2]->read();
Serial.printf(">SG (ch2) - Value: %.2f\n", data);
delay(250);
}
Example 1: Reading a PT1000 RTD sensor
#include "OpenIndus.h"
#include "Arduino.h"
AnalogLS analogls;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello OpenIndus !\n");
delay(1000);
// Add a two wire PT1000
analogls.addSensor(RTD_PT1000, {AIN_A_P, AIN_A_N});
// Set acquisition time to 50ms --> adc will sample input during 50ms and return a filtered value
analogls.sensors[0]->setAcquisitionTime(SAMPLE_50_MS);
// Wait 50ms before taking a sample for signal to establlish (through external RC filter for example)
analogls.sensors[0]->setStabilizationTime(50);
}
void loop(void)
{
float data = 0.0;
/* RTD */
data = analogls.sensors[0]->readTemperature();
Serial.printf(">RTD (CH0) - Temperature(°C): %f\n", data);
delay(200);
}
Example 2: Reading a Type K Thermocouple
#include "OpenIndus.h"
#include "Arduino.h"
AnalogLS analogls;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello OpenIndus !\n");
// Add a type K thermocouple
analogls.addSensor(THERMOCOUPLE_K, {AIN_E_P, AIN_E_N});
}
void loop(void)
{
float data = 0.0;
data = analogls.sensors[0]->readMillivolts();
Serial.print(">TC (CH0) - Voltage (mV): ");
Serial.println(data);
data = analogls.sensors[0]->readTemperature();
Serial.print(">TC (CH0) - Temperature (°C): ");
Serial.println(data);
delay(250);
}
Example 3: Reading a Strain Gauge
#include "OpenIndus.h"
#include "Arduino.h"
AnalogLS analogls;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Hello OpenIndus !");
/* Add a strain gauge : SIGNAL+ SIGNAL- EXCIT+ EXCIT- */
analogls.addSensor(STRAIN_GAUGE, {AIN_B_P, AIN_B_N, AIN_A_P, AIN_A_N});
}
void loop(void)
{
Serial.print(">SG value: ");
Serial.println(analogls.sensors[0]->read());
delay(250);
}
Software API
AnalogInputsLS Class
-
class AnalogInputsLS
Public Static Functions
-
static int addSensor(Sensor_Type_e type, std::vector<AIn_Num_e> ainPins)
Add a new sensor.
- Parameters:
type – [RAW_SENSOR; RTD_TWO_WIRE; RTD_THREE_WIRE; THERMOCOUPLE[B|E|J|K|N|R|S|T]; STRAIN_GAUGE]
ainPins – a vector that contains the pins set by the user
- Returns:
int the index of the added element (first call to this function will return 0, second call 1, …). return -1 in case of error
-
static int listSensors(void)
Lists all sensors.
- Returns:
nbr of sensors
-
static inline void resetSensors(void)
Reset the sensor list.
- Returns:
void
-
static int addSensor(Sensor_Type_e type, std::vector<AIn_Num_e> ainPins)
RTD Class
-
class RTD : public Sensor
Raw Sensor Class
Thermocouple Class
-
class Thermocouple : public Sensor
Strain gauge Class
-
class StrainGauge : public Sensor
Public Functions
-
float read(bool print_result = false)
Read the strain gauge value.
- Parameters:
print_result – true to print the result
- Returns:
float the strain gauge value
-
void setParameter(Sensor_Parameter_e parameter, Sensor_Parameter_Value_u value)
Set the parameter of the strain gauge.
- Parameters:
parameter – the parameter to set
value – the value to set
-
float read(bool print_result = false)
Available Sensor Types
RTD_PT100: Platinum RTD with 100Ω resistance at 0°C
RTD_PT1000: Platinum RTD with 1000Ω resistance at 0°C
THERMOCOUPLE_B: Type B thermocouple (250°C to 1820°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_E: Type E thermocouple (-200°C to 1000°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_J: Type J thermocouple (-210°C to 1200°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_K: Type K thermocouple (-270°C to 1372°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_N: Type N thermocouple (-200°C to 1200°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_R: Type R thermocouple (-50°C to 1768°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_S: Type S thermocouple (-50°C to 1768°C)
THERMOCOUPLE_T: Type T thermocouple (-200°C to 400°C)
STRAIN_GAUGE: Strain gauge sensor